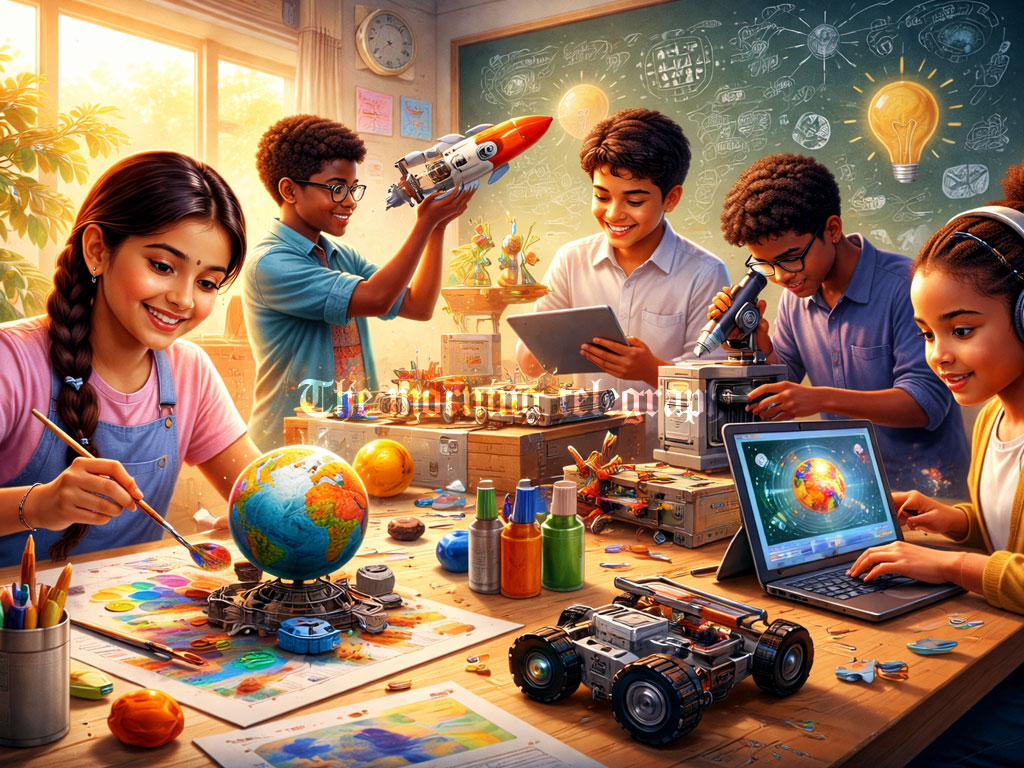
Creativity is quietly reshaping academic success, helping students think deeper, learn smarter, and prepare for a future where innovation matters more than memorization.
Parents play a crucial role in nurturing creativity from an early age. When adults collaborate with children on planning activities, problem-solving tasks, and everyday decisions, creativity becomes part of daily life rather than a classroom concept. Asking thoughtful, open-ended questions and treating mistakes as opportunities to learn helps children develop an open and confident mindset that supports both academic achievement and personal growth.

Why Creativity Matters
In today’s education system, grades alone no longer define a student’s success. While academic scores remain important, qualities such as critical thinking, problem-solving, adaptability, and innovation have become equally essential. At the center of this shift lies creativity. Creativity allows students to generate new ideas, approach challenges from different angles, and think beyond traditional methods of learning. It is not confined to drawing, music, or performance. Creativity plays a central role in science, technology, mathematics, language learning, and social studies.
Students who integrate creativity into their learning tend to understand concepts more deeply. They retain information for longer periods and often perform better in assessments because they truly grasp the subject rather than memorizing facts. In a world that is changing rapidly due to technology, globalization, and new career demands, students and parents alike must recognize creativity as a powerful tool for both academic success and personal development.
What Is Creativity?
Creativity is the ability to use imagination, knowledge, and thinking skills to develop ideas that are new, useful, and meaningful. It often involves stepping away from standard approaches to problem-solving and exploring alternative paths. For example, solving a mathematics problem using a method different from the one taught in the textbook, or explaining a scientific concept in one’s own words, reflects creative thinking.
When students practice creativity, they strengthen analytical thinking and problem-solving skills while learning to express ideas clearly and precisely. Creativity also builds self-confidence and independence, encouraging students to ask themselves, “What happens if I try it differently?” This mindset allows learners to see both success and failure as valuable parts of the learning journey. Solving a problem in an unconventional yet effective way demonstrates that creativity and academic excellence can work hand in hand.
Various Forms of Creativity
Creativity appears in many forms, including art, music, literature, scientific research, technological design, social innovation, and language use. In Sri Lanka, schools often involve students in science exhibitions and art displays that promote discovery, experimentation, and problem-solving. These activities encourage students to apply classroom knowledge in practical and imaginative ways.
Digital fields such as computer programming, robotics, animation, and game design offer powerful platforms for creative expression. Through these fields, students develop innovative ideas and compete successfully at national and international levels. Every student possesses at least one creative talent, and schools increasingly encourage participation in speech competitions, drama, debates, and exhibitions to nurture these abilities.
Educational systems are gradually shifting focus from grades alone to meaningful experiences. This change helps students appreciate creativity in multiple forms. For instance, Sri Lankan circus artist Lakshman Mello inspired generations through his unique performances, demonstrating how creativity can influence culture and leave a lasting impact beyond formal education.
How Creativity Supports Academic Growth
Creativity strengthens academic learning in several important ways. It enables students to understand lessons more deeply, builds confidence by encouraging experimentation, and develops strong critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Creative learning also increases classroom engagement and helps students develop planning and organizational abilities.
When students write historical events as stories, they tend to remember details longer. Solving mathematics problems in multiple ways improves analytical thinking and flexibility. Parents can support this growth by asking open-ended questions such as, “What do you think?” or “How would you solve this?” rather than providing immediate answers.
Mistakes are essential to the learning process. When students feel safe making errors, they are more willing to experiment and explore. Technology, including educational apps and online research tools, can further foster creativity when used with clear purpose and guidance.
Group Work and Social Creativity
Creativity becomes even stronger when students work together. Collaboration teaches learners to listen to different perspectives, communicate ideas clearly, and respect the opinions of others. Group activities help students understand that creativity is not only individual but also collective.
In Sri Lanka, students regularly showcase creativity through science fairs, speech contests, and art competitions. These experiences boost academic performance while building confidence and communication skills. Group projects, debates, and community service initiatives allow students to combine ideas and apply creativity to real-life challenges. At the same time, these activities develop leadership qualities and a sense of social responsibility.
Creativity in the Global Arena
Around the world, creativity has become a highly valued competitive skill. Employers and educational institutions in countries such as the United States, Germany, and Japan increasingly prioritize innovative thinking and the ability to apply ideas over rote memorization. The modern workplace values individuals who can adapt, problem-solve, and think creatively in complex situations.
Universities now assess students not only on grades but also on projects, inventions, research, and community involvement. Students who develop creativity early in their education are better prepared to compete globally. In Singapore, creativity-focused educational programs strengthen students’ competitive abilities, contributing to both academic achievement and personal success.
Creativity Development Initiatives in Sri Lanka
Many Sri Lankan schools and educational centers actively promote creativity through science days, exhibitions, competitions, drama, music programs, and art festivals. Project-based learning, group work, and community service initiatives help students develop innovative thinking, leadership skills, and problem-solving abilities.
Some institutions collaborate with international organizations to offer global exposure through science and technology competitions. These initiatives allow students to test their skills beyond national boundaries and gain confidence in expressing their ideas academically and socially.
Integrating Creativity into the Curriculum
Creativity should be embedded within the curriculum rather than treated as an optional or separate skill. Activities such as creative writing in language classes, research projects in science, solving mathematical problems using different methods, and role-playing historical events make learning more meaningful and engaging.
When creativity is part of everyday learning, students develop a deeper understanding of subjects. They build confidence, improve critical thinking, and acquire practical problem-solving skills that support long-term academic success.
Technology and Creativity
Technology is a powerful tool for nurturing creativity when used thoughtfully. Programming, animation, video editing, digital storytelling, and online research encourage innovation and exploration. Parents and educators should ensure technology is used for educational and creative purposes rather than excessive gaming or passive consumption of social media.
In countries such as India and South Korea, students design apps, participate in coding competitions, and achieve international recognition. These examples highlight the benefits of combining creativity with technology to prepare students for future careers.
Parents’ Role in Nurturing Creativity
Parents play an essential role in shaping a child’s creative mindset. Working with children on planning activities, encouraging curiosity, and treating mistakes as learning opportunities helps children develop confidence and resilience.
Simple activities such as reading together, storytelling, drawing, cooking, or family discussions stimulate cognitive development. Recognizing that each child learns differently and avoiding unhealthy comparisons creates a supportive environment where creativity can flourish at home.
Recommended Activities for Students
Students can strengthen creativity through a variety of activities, including writing essays or stories, conducting research projects, practicing art, music, or drama, and learning computer coding. These activities encourage exploration and perseverance.
Experiencing failure in creative tasks teaches resilience. Asking, “How can I do this differently?” helps students develop flexible thinking that benefits both academics and life. Planning exercises, creative problem-solving tasks, and presentation projects further enhance critical thinking skills.
Future Education and Creativity
Future education and career paths will increasingly value creativity, adaptability, and innovation. As artificial intelligence and automation expand, human creativity becomes a defining advantage. Individuals who can think creatively will be better equipped to navigate global challenges.
Beyond technology, skills such as teamwork, communication, and research enable students to take initiative and innovate. Developing creativity today is an investment in tomorrow’s academic, professional, and personal success.
Challenges and the Path to Growth
Developing creativity is not without challenges. Students may feel uncomfortable abandoning familiar methods or fear failure and competition. Limited time, resources, or support can also restrict creative exploration.
However, group activities, imagination exercises, and small creative projects help students overcome these barriers. Learning to face failure and try again strengthens perseverance and innovation. Failure becomes a stepping stone rather than a setback, laying the foundation for lifelong creativity.
Turning Creativity into Academic Success
Creativity is a powerful tool for academic success. Students who apply creative thinking understand lessons more deeply, generate multiple solutions, learn from mistakes, and develop strong self-confidence. Creative learners are more engaged and motivated, which positively impacts academic performance.
When parents and teachers work together to guide students, creativity can be directed toward achieving academic excellence and personal growth. Creativity not only supports success in school but also equips students with skills needed to thrive in life and contribute meaningfully to society.
Final Word
Creativity is not an optional skill. It is a vital foundation for academic success and lifelong learning. Creativity empowers students to think independently, solve problems effectively, and approach challenges with confidence and flexibility.
When creativity is nurtured at home, supported in schools, and integrated into the curriculum, students move beyond rote memorization toward meaningful understanding. In a rapidly changing world driven by innovation and technology, creative thinkers are better prepared to adapt, excel, and lead. By valuing creativity alongside academic achievement, parents, teachers, and students together can shape a future where learning is deeper, more engaging, and truly transformative.